Location: 首页 > Applications > Water diversion project

Water conservancy engineering facilities that draw water from water sources to irrigate farmland. According to the difference of river water volume, water level and elevation of irrigation area, it can be divided into two types: non-dam diversion and dam diversion. The planning and layout of the water diversion hub should meet the following requirements: adapt to the fluctuations of river water level and meet the requirements of irrigation water consumption; the irrigation water entering the channel has a low sand content; the structure of the water diversion hub is simple, the main canal is short, the cost is low and it is convenient for construction and management; the location is in good geological conditions, the river bank is firm, the river bed and mainstream are stable, the soil is dense and uniform, and the bearing capacity is strong.
Since the main stream of the river channel is always close to the concave bank, the canal head diversion project is generally located downstream of the midpoint of the concave bank of the river channel, and the angle between the center line of the diversion channel and the main stream line of the river channel is not more than 30°-40°. In this way, the lateral circulation effect of the bend can also be used to prevent sediment from silting at the mouth of the canal and to prevent the bottom sand from entering the canal, avoiding the top rushing part of the concave bank. When the canal head diversion project cannot be arranged on a concave bank but must be placed on a convex bank due to the location of the irrigation area and topographical conditions, the canal head can be placed upstream of the midpoint of the convex bank, where there is less sedimentation and at the same time engineering measures such as lengthening the diversion dike to the main stream can be used to create "artificial circulation" and lead water into the canal.
Dam-free water diversion
The water level and flow of the river can meet the water intake requirements, and there is no need to build a dam to raise the water level. It is generally composed of inlet gates, sand flushing gates and diversion dikes. The intake gate is used to control the flow into the main canal and prevent the bottom sand from entering the main canal. The flushing gate is used to flush the sediment deposited in front of the intake gate, and the water discharged through it creates an artificial circulation, fixes the direction of the main stream of the river, and discharges the excess water during the flood. The diversion dike is used to guide the water flow smoothly into the intake gate, and part of the water overflows from the diversion dike during the flood. Intake gates and sand flushing gates are always close together, and their mutual positions in the canal head project generally have two arrangements: ①Sand discharge on the front and water diversion on the side. When the river has a large amount of water and a lot of sand, in addition to ensuring the irrigation water in the irrigation area, there is enough flow to flush the sand or water distribution to the downstream irrigation area is often arranged in this form. The direction of its discharge is the same as that of the main flow. The axis of the inlet sluice and the main flow form an acute angle, generally 30°~40°, to reduce the impact of flood on the inlet sluice, while the flushing sluice can effectively wash away the deposits at the head of the canal. Of sand. ②Divert water on the front and discharge sand on the side. When the water volume of the river is small and the irrigation area is large, the arrangement in this form can increase the inflow flow. The axis of the inlet sluice is consistent with the main flow direction, while the flushing sluice is at a large angle (close to 90°) with the main flow direction. At this time, more sand and gravel enter the canal, and the longitudinal slope of the main canal must be enlarged, and appropriate sand flushing gates should be arranged along the canal line. The arrangement of the diversion dike starts from the sluice gate and extends to the upstream river course to approach the main stream, so that the main flow enters the canal along the diversion dike. The appropriate angle between the diversion dike and the main flow is 10°~30°. If it is too large, the dike will be easily destroyed by flooding and affect the water diversion; if it is too small, it will increase the length of the diversion dike and increase the amount of work.

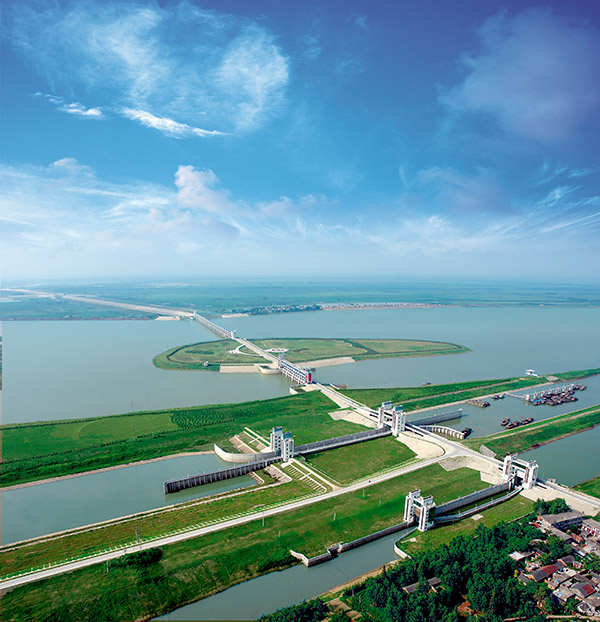
In general, only one water intake is built for non-dam diversion, which is called single-head system. In the case of unstable riverbanks and riverbeds, or where the water source contains a lot of sand, the multi-head system can be used to divert water. The construction of the hub is relatively simple, it can take local materials, and does not require high geological conditions. It is suitable for river downstream or plain areas where the river has abundant water sources and the water level and flow can meet the requirements of irrigation water. The famous Dujiangyan Water Conservancy Project in China is an example of a non-dam diversion irrigation project (see color picture). Dujiangyan was built during the Warring States Period, and its water diversion hub is composed of Baizhang Dike, Yuzui, Jingang Dike, Feishayan, Baopingkou and other projects (see picture). Yuzui and Jingangdi divide the Minjiang River into two branches, Neijiang and Waijiang. The outer river is the main stream of the Minjiang River, and the inner river is the water diversion channel for irrigation. According to the changes in the flow and water level of the Minjiang River, the fish mouth can naturally divide water at a ratio of four to six. In the irrigation season, the inner river divides 60% of the water and the outer river divides 40%; during the flood period, the inner river divides the water into four and the outside six, thus ensuring the irrigation and flood diversion requirements of the irrigation area. The Baizhang Dike was built on the east side of the upper reaches of Yuzui to protect the curved river bank and guide the flow of water. The Feisha Weir is about a hundred meters wide. When the water intake in the Neijiang River is greater than the irrigation water consumption, the excess water will be discharged by the Feisha Weir, which plays a role of spillway and sand removal. Baopingkou is the water intake of the Neijiang River. It is located downstream of the apex of the concave bank of the Minjiang Bend. It can draw surface water by using lateral circulation. The Dujiangyan water diversion hub stretches for about 3 kilometers from Baizhang Dike to Baopingkou. Various engineering facilities are closely coordinated and coordinated to work with each other, which has played a good effect of water diversion and flood discharge,
water diversion and sand prevention.
When the water source of the river is abundant, but the water level cannot meet the irrigation requirements, it is necessary to build a backwater structure (dam or sluice) on the river course to raise the water level so as to divert the water for artesian irrigation. A dam diversion hub is mainly composed of buildings such as a barrage, an intake gate, a sand flushing gate, and a flood control embankment. In addition, in order to meet the needs of comprehensive utilization of the river, buildings such as ship locks, fish passages, raft passages and power stations can also be set up. The function of the barrage is to cross the river channel and raise the water level to meet the requirements of irrigation and diversion; during the flood season, it overflows at the top of the overflow dam to discharge the river flood. Therefore, the dam crest must have a sufficient overflow width. When the width is restricted or the upstream backwater should not be too high, the height of the dam crest can be lowered and replaced by an overflow dam or barrage with gates to increase the flood discharge capacity. The intake gate is used to divert water for irrigation. Its layout is the same as that of water diversion without dam. The flushing sluice is an indispensable part of the low-dam diversion hub of the sand-laden river, and it is placed on the river bed between the inlet sluice and the overflow dam. Its water passing capacity should be greater than that of the inlet sluice, and the floor elevation should be lower than that of the inlet sluice to ensure a good sand flushing effect. Flood prevention dikes are mostly built along the upper reaches of the barrage along the river, and their role is to reduce the inundation loss of the upper reaches of the barrage, and protect the upstream towns and traffic safety during the flood period.
The dam diversion project is closer to the irrigation area and the main canal is short, which can effectively control the water level of the river and increase the reliability of water diversion. In 422 BC, Ximenbao led the construction of the Twelve Canal of Zhangshui in Weiye (now Ci County and Linzhang County, Hebei), which was a dam diversion and irrigation project. China's larger dam-diversion irrigation areas include Shaoshan Irrigation District in Hunan Province, Nanwan Irrigation District in Henan Province, Baojixia Irrigation District, Jinghuiqu Irrigation District, Luohuiqu Irrigation District in Shaanxi Province, etc.

 Jing12011202000600 Website construction: Fengsheng Technology
Jing12011202000600 Website construction: Fengsheng Technology